Raycast
What is Raycast
In a collision detection scenario, a raycast can be used to determine whether a line of sight exists between two objects or whether a collision is imminent. By casting a ray from one object to another, the physics engine can determine whether the ray intersects with any other objects in its path, allowing the game to determine whether the two objects can "see" each other or whether a collision has occurred.
How to use it
Here is an example of raycast:
var raycastResult = new BABYLON.PhysicsRaycastResult();var start = new BABYLON.Vector3(1, 20, 2);var end = new BABYLON.Vector3(1, -20, 2);physicsEngine.raycastToRef(start, end, raycastResult);if (raycastResult.hasHit) { console.log("Collision at ", raycastResult.hitPointWorld);}The important thing to note here is the raycastResult that can (and should!) be reused between calls. This is the major difference with Physics V1 raycasting.
The result object has some information about the properties of the intersection, such as the intersection point, the body that was hit, and the index of the triangle hit in case it hit a Mesh Shape. You can find all the fields in the PhysicsRaycastResult class.
RayPicking Vs RaycastRaycast queries
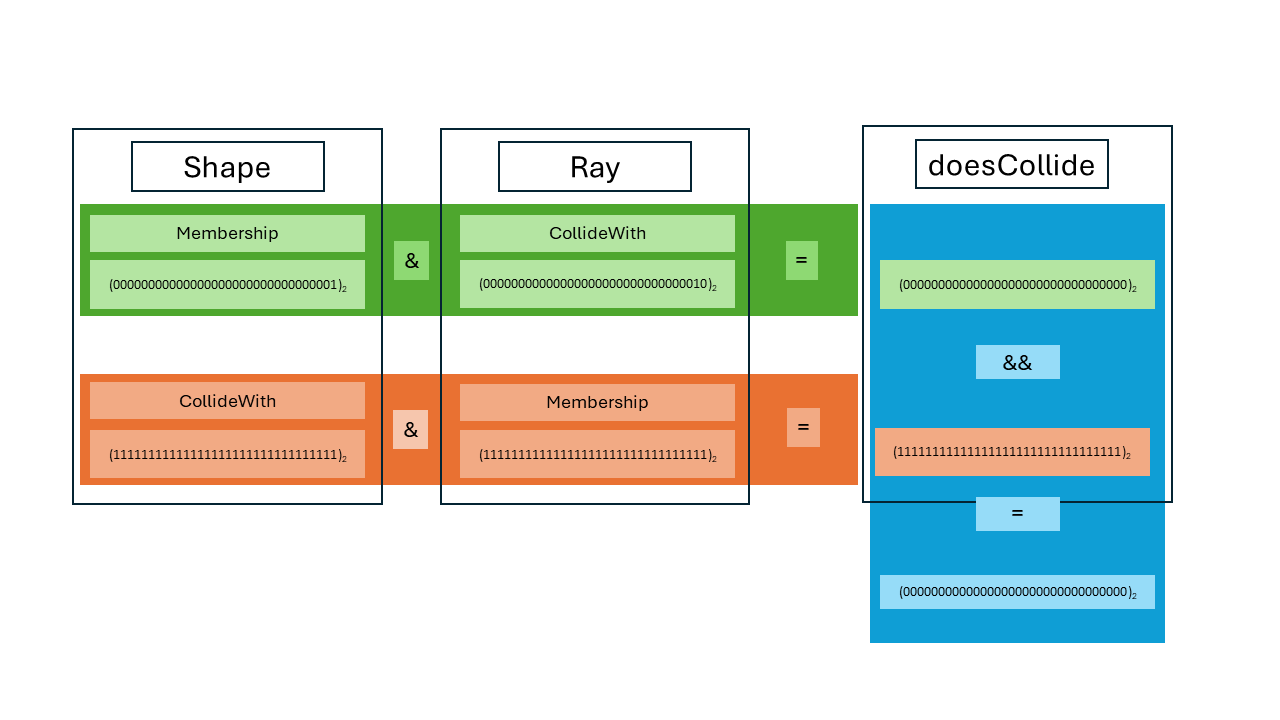
You can use raycast queries to make the raycast test for specific objects only. The test utilizes the membership and collideWith fields, as follows:
bool doesCollide = (ray.membership & shape.collideWith) && (shape.membership & ray.collideWith)Where & represents the bitwise AND operation and && the logical AND. By default, if not specified, the values for both the membership and collideWith fields are 0xffffffff, which is the identity for the bitwise operation.
var shapeA = new PhysicsShape(...);var shapeB = new PhysicsShape(...);
shapeA.filterMembershipMask = 1; // 01 in binaryshapeB.filterMembershipMask = 2; // 10 in binary
/** * EXAMPLE 1: will test only for shape A */physicsEngine.raycastToRef(start, end, raycastResult, {collideWith: 1});
/** * EXAMPLE 2: will test only for shape B */physicsEngine.raycastToRef(start, end, raycastResult, {collideWith: 2});
/** * EXAMPLE 3: will test for shape A AND shape B (as 3 is 11 in binary) */physicsEngine.raycastToRef(start, end, raycastResult, {collideWith: 3});Here's a diagram of the operation for the second example's test on shapeA (which does not collide with the ray):